Cyberattacks are no longer rare events. They target businesses, individuals, and even public institutions every day. Understanding how to prevent cyberattacks is no longer optional; it’s a necessity if you want to protect sensitive data and keep your systems running.
This guide explains the most common types of cyberattacks, how they work, and the cybersecurity best practices you can apply right now to reduce your risk.

Why Prevention Is More Effective Than Recovery
A cyberattack can create problems that take a lot of time and money to fix. The damages can go far beyond the financial losses and touch an organization’s reputation, its trust with customers, and even its ability to keep the doors open. For a beleaguered organization, tempted to save some cash by cutting a few corners, the possibility of turning a short-lived disaster into a long-term one could easily tip the scales against saving money.
Basic weaknesses, such as not having up-to-date software, having weak passwords, or having employees who are not aware of cybersecurity risks, are being exploited by cybercriminals. Fixing these vulnerabilities is the simplest way to significantly cut your chances of getting hit.
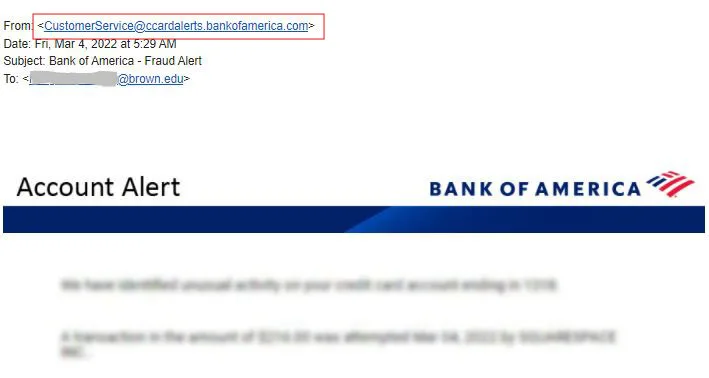
Phishing Attacks: The Most Frequent Threat
One of the major techniques hackers use to get into systems is phishing. A phishing email or message is crafted to look real, and it tries to get the recipient to click on a bad link or give up private information.
How to Avoid Phishing Attacks
- Double-check the sender’s address for accuracy.
- Hover over links to verify their true destination before clicking.
- Avoid downloading attachments from unknown senders.
- Provide regular training so employees can spot and report phishing attempts.
Education is one of the most effective defenses. Even the best security software can’t stop someone from clicking the wrong link, so awareness matters.
Ransomware: Holding Data Hostage
Ransomware is malicious software that encrypts your files and demands payment for access. Even if the ransom is paid, there’s no guarantee the files will be restored.
Ransomware protection starts with preparation. Keep encrypted backups stored offline so attackers can’t access them, and make sure software updates are applied promptly to patch known weaknesses. Use security tools with real-time scanning to detect suspicious file activity before it spreads. Finally, limit file access so only authorized users can change or delete critical information.
Preparedness is key here. If your backup strategy is strong, you can recover quickly without paying a ransom.

Malware Infections: Silent and Dangerous
There are numerous kinds of malware: viruses, spyware, trojans, and they can operate quietly in the background, pilfering data or harming systems.
To cut down risk, steer clear of obtaining files from unrecognized sources and ensure that your protection software is up to date. Perform regular scans with it and deny entry to any sites that seem suspicious. These rudimentary precautions are your best line of defense, stopping malware from getting into your system and wreaking havoc.
DDoS Attacks: Overloading Your Systems
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is like hundreds of thousands of fake “visitors” rushing into your store at the same time. None of them are real customers; they’re just there to block the doorway so genuine customers can’t get in.
On the internet, this means your website or network is overwhelmed with so many connection requests that it slows down or stops working completely. The attacker’s goal isn’t to steal information but to make your service unavailable, which can frustrate users, interrupt sales, and cause financial losses.
Preventing a DDoS attack involves two main steps:
- Infrastructure tools like a Content Delivery Network (CDN), which spreads incoming traffic across multiple servers so no single one is overloaded.
- Security settings, such as firewall rules that block suspicious or repetitive requests before they reach your system.
Finally, having real-time monitoring in place means you can spot sudden traffic spikes early and respond before the attack brings everything to a halt.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Intercepting Data
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks occur when a hacker intercepts communication between two parties. This often happens on unsecured Wi-Fi networks and can lead to stolen login credentials.
Protect yourself by only using websites with HTTPS, encrypting sensitive communications, and using a virtual private network (VPN) on public connections. These steps make intercepted data far less useful to attackers.
SQL Injection: Targeting Databases
The stored information is accessed or changed by what are essentially clever attacks on poorly programmed websites. They can and do steal sensitive data, including customer records, and payment information. Since many businesses now store all their data in some kind of database, a successful SQL injection attack can mean not just identity theft and credit card fraud; it can also mean that a business may find itself on the brink of bankruptcy.
Preventing SQL injection requires using parameterized queries, keeping database software updated, and installing a web application firewall. Regular vulnerability testing also ensures weaknesses are addressed before hackers find them.
Credential Stuffing: Using Stolen Logins
If you reuse passwords across multiple accounts, credential stuffing attacks can cause major problems. Hackers use login details stolen from one site to break into accounts on another.
Defenses against this threat work best when every account has a unique password and, even better, when multi-factor authentication is used. For many people, memorizing unique, strong passwords for all of their accounts is a big ask. And that’s where a password manager can come in.

Cybersecurity Best Practices That Work Across All Threats
While each attack has specific countermeasures, there are core actions that strengthen overall security:
- Keep all systems, applications, and devices updated.
- Encrypt sensitive data both during transfer and while stored.
- Remove accounts and permissions that are no longer needed.
- Provide ongoing cybersecurity best practices training for employees.
These measures create layers of defense, making it harder for attackers to find an easy way in.
Why Work With TechFusion to Learn How to Prevent Cyberattacks
Some cyber threats are too advanced for basic defenses. TechFusion offers advanced monitoring, incident response, and proactive threat detection tailored to your needs. Our team can conduct in-depth audits to identify weak spots and implement systems that detect and respond to threats in real time. Contact TechFusion now for a professional cybersecurity assessment.
Stay Ahead of Cybercriminals
Preventing cyberattacks is a process that takes constant attention and effort. The changes that happen in this area can be very rapid indeed. The methods used by the bad guys can change from one day to the next. A sufficient level of attention spans many different activities.
Avoid waiting until a breach has occurred to act. Review your existing defenses, tighten any weak spots, and forge a plan to meet future threats head-on. TechFusion can help you establish and retain a strong security posture that adapts to an ever-evolving threat landscape. For assistance, call us at 617-284-0884 or reach out to get help from our expert team.
Frequently Asked Questions: How to Prevent Cyberattacks
What’s the difference between a cyberattack and a data breach?
A cyberattack is any attempt to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to a system. A data breach happens when sensitive information is actually stolen or exposed during an attack.
Can using public Wi-Fi increase my risk of a cyberattack?
Yes. Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making it easier for attackers to intercept your data. Use a VPN when connecting on public networks to encrypt your activity.
How often should I update my passwords?
Change your passwords every 3–6 months, and right away if you have any reason to think they’ve been compromised. Use different, complicated passwords for each of your accounts, and safeguard those passwords, to reduce the risk from attacks that rely on using unfound yet valid credentials.
Are small businesses really targeted by cybercriminals?
Absolutely. Many attackers target small businesses because they often have weaker defenses than large corporations. Implementing strong cybersecurity best practices is just as important for smaller operations.
What should I do first if I suspect I’m under attack?
Disconnect affected devices from the network to contain the problem, change your passwords from a secure device, and contact your IT team or a cybersecurity professional immediately. Acting quickly can limit the damage.